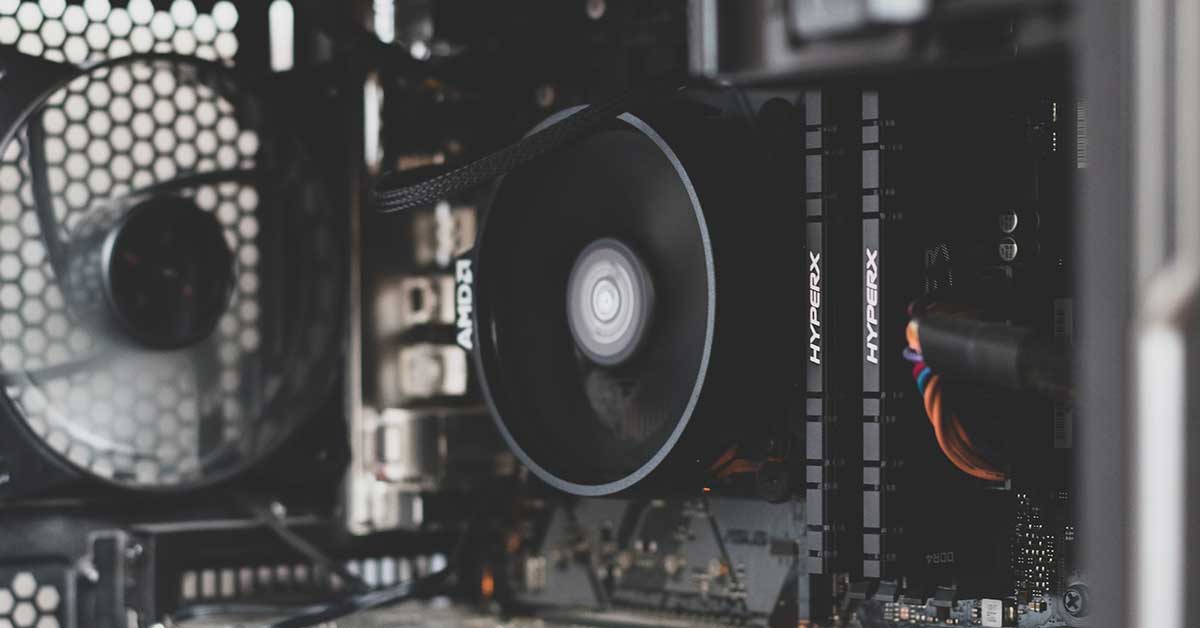
Have you ever checked your CPU temperature after hours of heavy gaming or CPU-intensive rendering/ video editing applications? If the answer is no, you can check your CPU’s temperature in BIOS/UEFI or use any third-party software such as HWMonitor, Core Temp, etc.
If you’re running at 50-60OC, then you’re good to go, but when you exceed +90OC after heavy gaming then you should take immediate action to lower your CPU temperature. Because CPU’s high temperature not only decreases performance but also shortens the PC lifecycle.
Every running electronic chip produces more or less heat due to the nature of the silicon and different types of coolers keep the chip temperature within a limit. But heavy gaming/workloads often push the CPU to use its 100% limit, generating massive overheating.
Of course, most modern CPUs have a thermal limit mechanism, at a specific temperature point CPU starts throttling to avoid burning. This fail-safe mechanism doesn’t work very well every time and the CPU melts in the motherboard.
There are several reasons for CPU overheating. In this article, we will explore what causes CPU overheating and how to fix them. If you’re running a PC for over a year and haven’t touched your computer for maintenance, it is high time to follow the steps below.
Contents
Remove dust from the CPU cooler
If your CPU temperature rises too high, there is a high probability that your cooler and heatsink have already become dusty. Use a soft brush or air blower to remove dust, these dust blocks cooler airflow and causes CPU overheating. A dusty heatsink can’t spread its heat properly so it goes back to the CPU and overheats. If you’re not in an air-tight room, you have to clean your CPU cooler as well as your full workstation at regular intervals to keep your processor cool.

Re-apply thermal paste
The thermal paste applied between the heatsink and processor becomes dry over the years and tiny air bubbles are born in the dried paste, these bubbles block heat conductivity between the CPU and heatsink. If you haven’t changed your thermal paste for a while, carefully remove the old paste and re-apply. Hopefully, it will reduce your CPU temperature significantly.
The quality of the thermal paste also plays an important role as some high-quality thermal paste can lower the temperature by about 3O-5OC than stock paste that comes with the CPU.
Limit CPU use
Modern AAA games and heavy VFX software need huge computing horsepower that drives the CPU to use 100% capacity. Running the CPU at 100% capacity for hours generates insane heat and temperature rises rapidly unless you have an extreme cooling solution. If dust cleaning and thermal paste re-apply don’t help much, and your weak processor can’t handle the heavy load continuously, you can simply limit your CPU use not to reach 100% capacity.
Go to the Control Panel and select the Small icon as shown above.
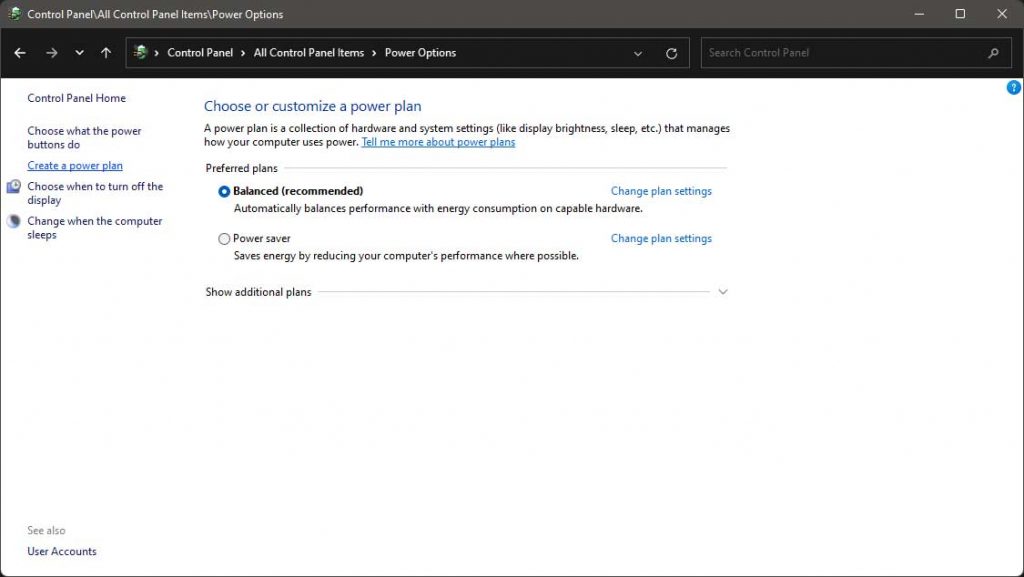
Click Power options and create a power plan
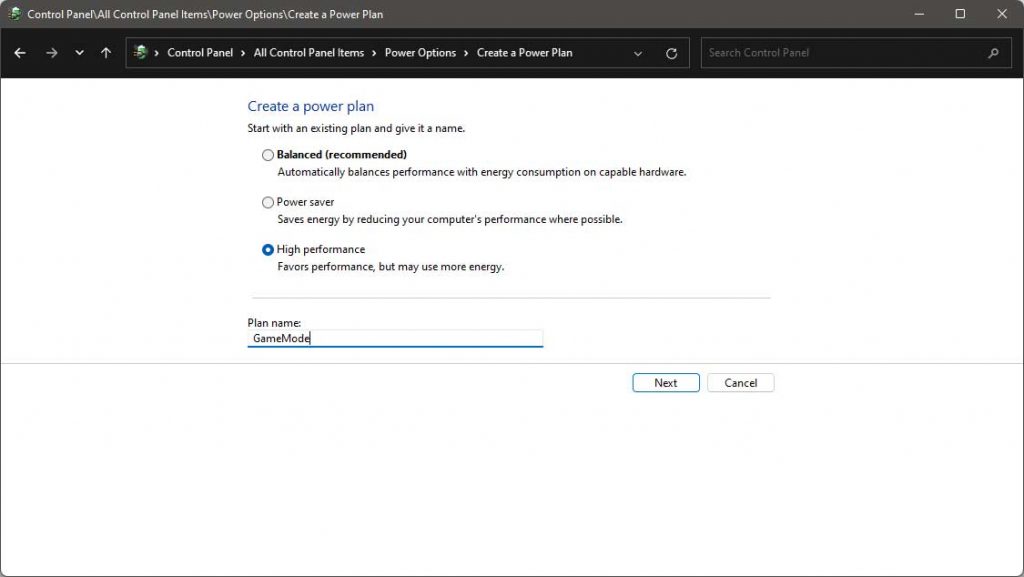
Select High Performance then set a custom plan name then create the profile
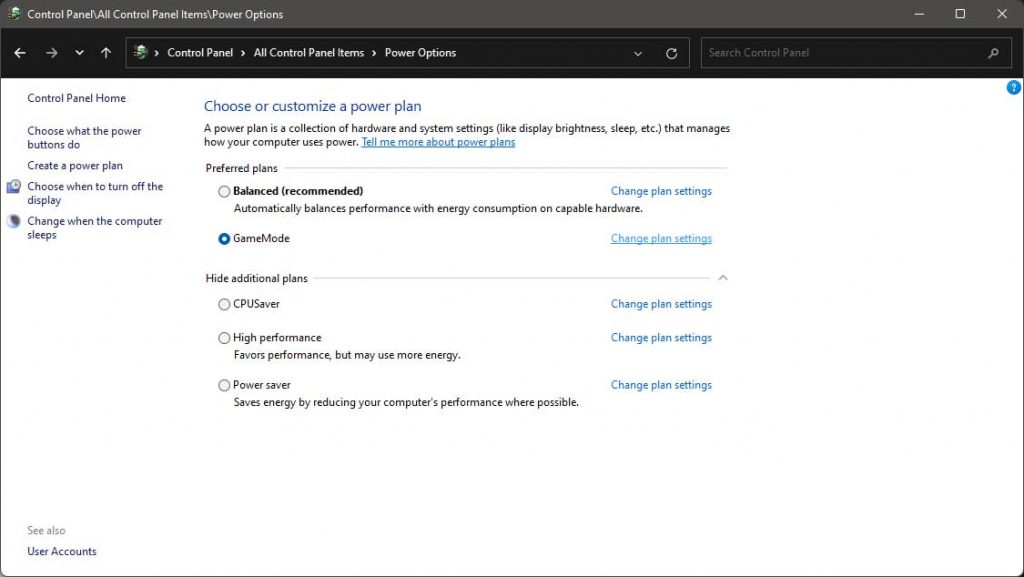
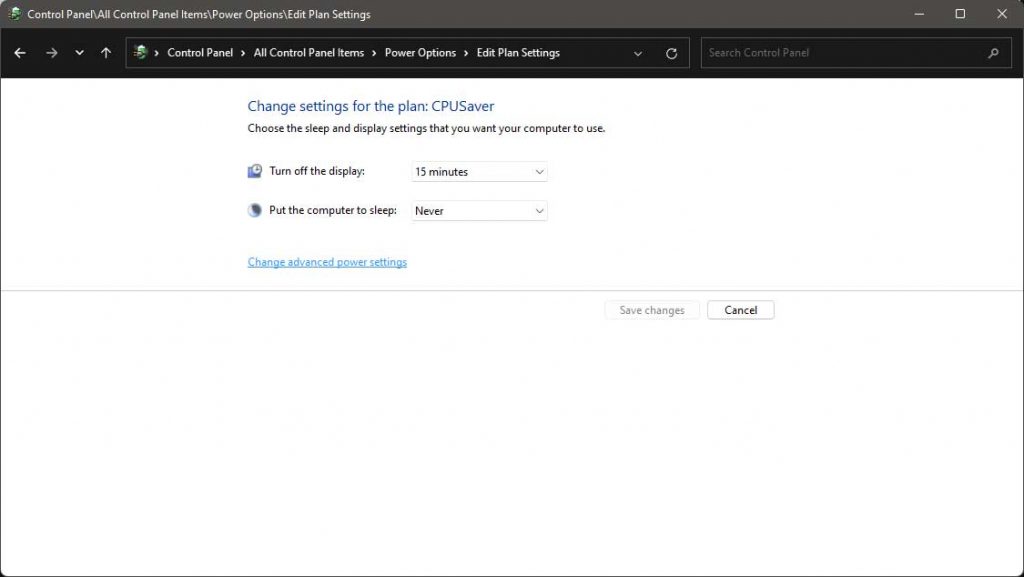
Change plan settings
Change advanced power settings
Select PCI Express> Link State Power Management> Moderate power savings
Select Processor power management> Set Minimum processor state to 80% and Maximum processor state to 90%
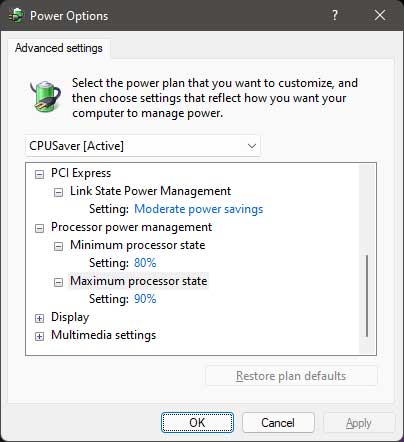
Click Apply> OK
You may get a few frames less in your games as we are going to limit CPU use to 90% but it will prevent CPU overheating.
Use an aftermarket CPU cooler
Unless you’re using an Intel K series or equivalent AMD high-end processor, there is a high chance that you’re using a stock cooler that comes with a CPU. Intel and AMD both companies don’t provide a stock cooler with their top-tier unlocked CPU and those CPU buyers have no option without an aftermarket CPU cooler.
The remaining of us barely buy a third-party cooler as we get a free one. Honestly, most of these stock cooler performance is terrible and they can’t dissipate generated heat properly. Some new AMD Wraith series stock coolers are pretty decent, Intel’s stock cooler’s performance still remains horrible.
Bundled stock CPU coolers have a relatively small heatsink and low-quality fan compared to aftermarket coolers. When the CPU reaches 100% load, the cooler’s fan runs at full speed to adjust the temperature and makes an annoying noise.
So, if you’re facing CPU overheating problems often, consider a decent aftermarket cooler. Your CPU will remain cool during gaming or any heavy workload such as video editing, rendering, etc. Now, liquid CPU coolers are popular among PC enthusiasts as they provide the best cooling solutions for high-end processors.
If you can afford a liquid cooler, simply go for it. Otherwise, you can choose a decent aftermarket AIR cooler and it will perform way better than your stock cooler.
Casing Airflow
Casing airflow is also important, due to improper airflow hot air inside the casing can’t get out and CPU temperature rises up. Make sure that your casing has proper airflow, and add some extra chassis fan if necessary. Wrong cable management sometimes blocks airflow, re-organize your cable management.
If your casing is small and no room left for extra chassis fans, get a modern casing that has excellent airflow. Let me know, which technique works for you.
Rob is a passionate tech enthusiast, reviewer, and content creator at techpowernext. With over a decade of experience in the tech industry, he dives deep into the latest gadgets, software, and innovations. His mission is to demystify complex tech concepts and empower readers to make informed decisions.

